Advanced Audit Policy Configuration in Windows Server lets you collect data on granular events at the server or AD domain level. In this post, we’ll teach you how to enable and use Advanced Security Audit Policy in Windows Server 2016 using Group Policies and the auditpol.exe utility.
Advanced Security Audit Policies debuted in Windows Server 2008 R2 (Windows 7) and allows you to enable more than 60 audit policies.
Configuring Audit Policies through Group Policy
Using the local Group Policy Editor in Windows Server 2016, you can see a list of possible audit policies.
Start the gpedit.msc console and navigate to the area below. Advanced Audit Policy Configuration > System Audit Policies > Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Advanced Audit Policy Configuration > System Audit Policies As you can see, there are ten different types of audit policies:
- Account Logon;
- Account Management;
- Detailed Tracking;
- DS Access;
- Logon/Logoff;
- Object Access;
- Policy Change;
- Privilege Use;
- System;
- Global Object Access Auditing.
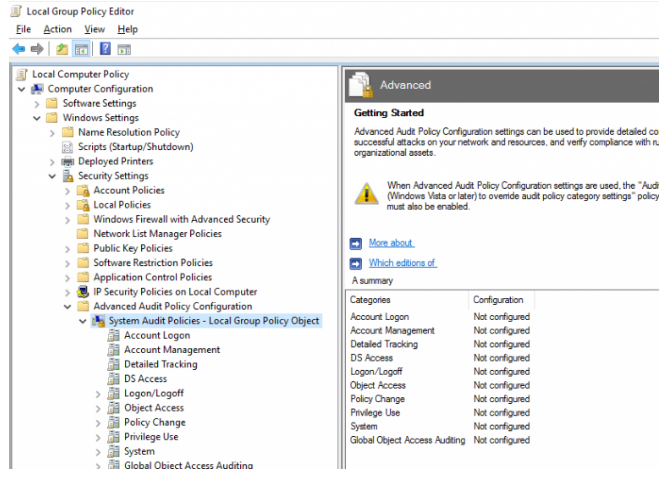
Each section has several audit event subcategories. For example, in the Account Management section there are several advanced audit policies:
- Audit Application Group Management;
- Audit Computer Account Management;
- Audit Distribution Group Management;
- Audit Other Account Management Events;
- Audit Security Group Management;
- Audit User Account Management.
All advanced audit policies are disabled by default.
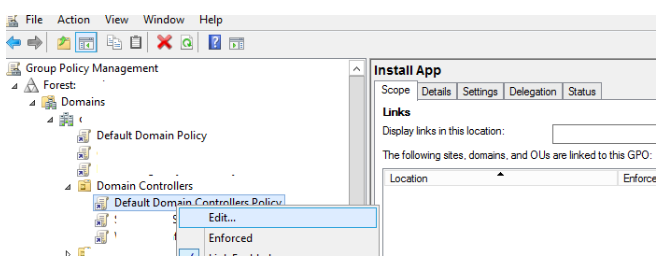
You could want to audit all change events in Active Directory security groups, for example. To do so, go to Default Domain Controllers Policy and enable the Audit Security Group Management policy. Expand Forest > Domains > yourdomain.com > Domain Controllers, right-click Default Domain Controllers Policy, and select Edit in the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc).
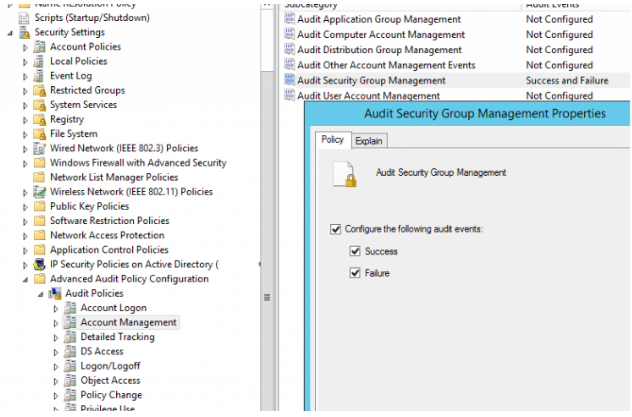
Select Audit Security Group Management from the GPO section Comp Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Advanced Audit Policy Configuration > Audit Policies > Account Management. Enable the policy “Configure the following audit events” and choose “Success” and “Failure” as security log events to be audited.
The gpupdate command can be used to update the group policy settings on the domain controller.
Try doing any operation with any AD group now (create group, change membership, etc.). Events from the Microsoft Windows security auditing source will appear in the Event Viewer > Windows Logs > Security log.
You can enable the event source filter (Right click Security > Filter Current Log > Enable Event Source Filter) for convenience. Task category: Security Group Management, Event Source: Microsoft Windows security auditing).
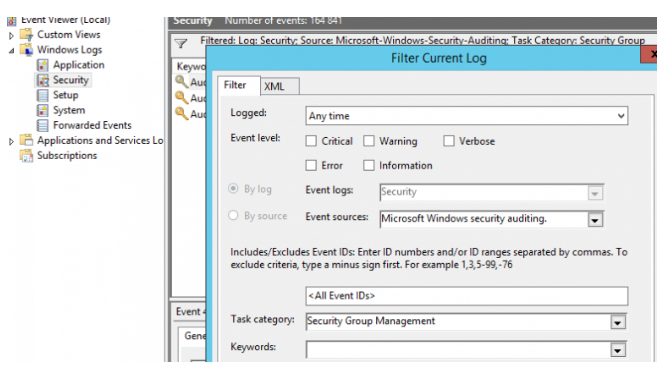
Only AD group administration events will now be recorded in the Security log, such as:
- EventID 4727 – A security-enabled global group was created;
- EventID 4728 – A member was added to a security-enabled global group;
- EventID 4729 – A member was removed from a security-enabled global group;
- EventID 4730 – A security-enabled global group was deleted.
The event description contains specific information on who made changes to the AD group and what changes were made.
Additional setting may be required for various sophisticated audit policies. To enable auditing of shared folder access (Object Access > Audit File Share), for example, you must also allow auditing in the folder attributes for which you want to gather audit events.
Manage Advanced Audit Policies with AuditPol
On a separate computer, you can view the current audit policies and enable/disable them using the built-in AuditPol.exe tool.
List all audit categories:
auditpol /list /category /v
Display a list of all audit subcategories:
auditpol /list /subcategory:*
Check if audit policies from the Object Access category are enabled:
auditpol /get /category:"Object Access"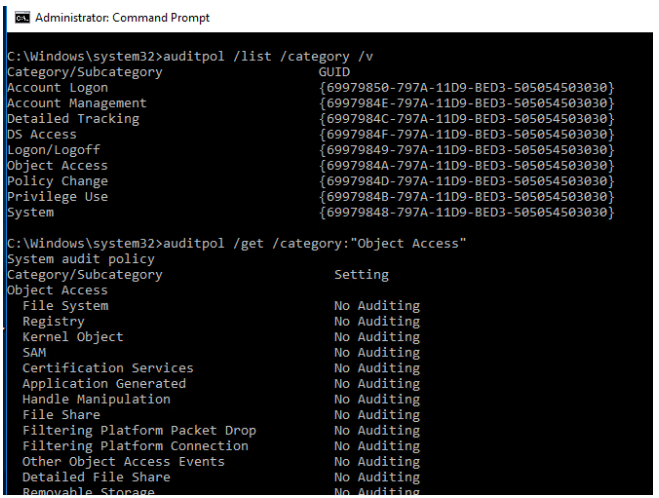
To enable registry access audit, use the following command:
auditpol /set /subcategory:"Registry" /success:enable /failure:enable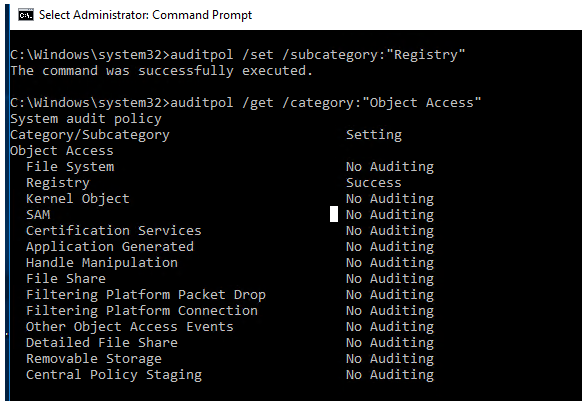
To disable an audit policy:
auditpol /set /subcategory:"Registry" /success:disable
You can save the current audit policy settings and import them to another computer/server using the /backup and /restore options.