The RID master (Relative Identifier) is one of three FSMO domain-level roles, which means that each domain must have at least one domain controller that possesses this role. A domain controller with the RID Master role is in charge of allocating a unique RID sequence to each domain controller in its domain, as well as ensuring that objects are correctly moved from one domain to the next. In other words, this job is responsible for assigning a unique SID (Security Identifier) to all Active Directory users, computers, and groups that uniquely identifies a user, group, domain, or computer account.
When an Administrator establishes a new item (new security principle) in Active Directory, it is given a unique Secure Identifier (SID). The new object’s SID is made up of domain SID and relative ID (RID), which is taken from the existing domain controller’s RID pool.
The RID master is in charge of issuing these one-of-a-kind domain identifiers. Each controller in the domain receives a pool of 500 relative IDs at a time (by default). The amount of RIDs issued and the request threshold can both be modified if necessary. The DC with the owner of the RID master role replenishes the pool if there are less than 50% of the identifiers left.
Display a list of all domain users’ SIDs, for example:
get-aduser –filter *|fl sidUsing the Dcdiag command, you can view the status of the RID master:
Dcdiag.exe /TEST:RidManager /v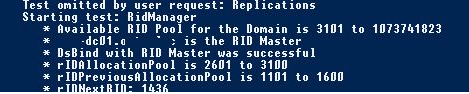
You can also view the current range of identifiers for current DC. By the way, on the other domain controllers the pool will differ (because each controller in the domain is given a unique pool).
Starting test: RidManager
* Available RID Pool for the Domain is 3101 to 1073741823
* dc01.domain.loc is the RID Master
* DsBind with RID Master was successful
* rIDAllocationPool is 2601 to 3100
* rIDPreviousAllocationPool is 1101 to 1600
* rIDNextRID: 1436
Moving things between domains is another area of responsibility for RID Master. RID Master prevents you from moving an object to two separate domains at the same time. Otherwise, there is a risk of two domains having two identical items with the same GUID, which might have disastrous implications.
When a security object travels from one domain to another, it assigns a new SID in the target domain, and the old one is recorded to the newly created attribute SIDHistory for history. This attribute contains the whole history of security identifier changes, and it can have several values.
- It is suggested, according to Microsoft Best Practices:
- On a single domain controller, keep the RID master and PDC emulator FSMO roles together.
- If you lose the RID master server for some reason, you can aggressively grab this position on any other domain controller, but keep in mind that the original RID master should no longer be visible on the network.
- Monitor events with EventID 16653-16658 are logged on domain controllers. They are expressing their dissatisfaction with the RID master’s job.
- If RID is unavailable, it will be unable to create new items in AD (at least for a while). The amount of time depends on the number of free SIDs left in the 500-piece packs.
Using the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, you can change the RID role owner.
- Connect to the DC to which you want to transfer the role using the ADUC console (Change domain controller).
- Select Operations Masters by right-clicking on the domain’s root.
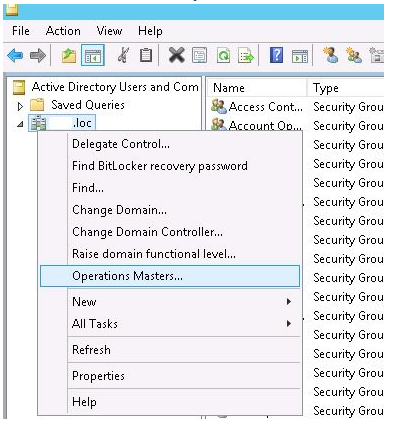
3. Press the Change button on the RID tab.
4. After that, you must confirm the transfer and wait for a message that the RID role has been successfully transferred.