The Conditional Access mechanism verifies each connection to the resource based on a specific scenario and a choice on what to do with that connection. You can restrict access, grant access without conditions, or provide access with conditions in a Condition Access policy.
When allowing a user access to a resource, Conditional Access allows you to utilise a variety of conditions:
Is the user a member of a particular Azure Active Directory group?
What cloud app is the user attempting to connect to?
Is it connected from a managed device (Intune/Hybrid Azure AD joined) or not?
Which IP address / subnet is the person attempting to connect from?
What kind of client is the user using (a computer app, a phone app, or a web browser)?
etc.
These parameters can be combined to ensure the highest level of security when accessing company resources.
Note: When creating Conditional Access policies, be cautious. To avoid losing access to Azure, it’s best to exclude the Global Admin group from your Conditional Access settings.
Conditional Access policies for Azure Active Directory (AD) are accessible with Microsoft 365 Business subscriptions (previously only available for Azure AD premium subscribers).
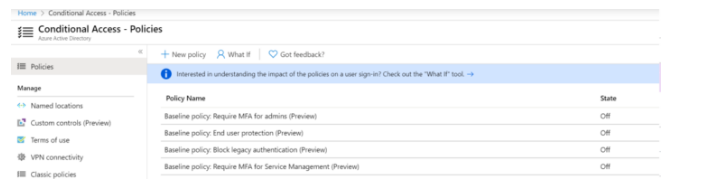
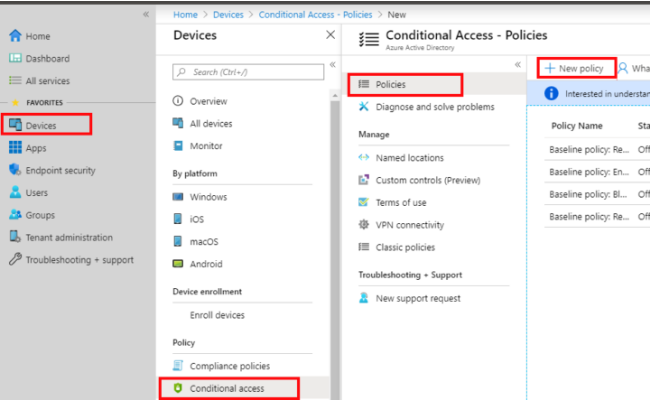
As an administrator, go to the Security > Conditional Access Policies area of your tenant.
Four Conditional Access preview policies are available even with a standard Azure subscription.
- Block access through legacy authentication protocols that do not support multi-factor authentication — the policy prohibits access via legacy authentication protocols that do not allow multi-factor authentication (MFA). For example, IMAP, POP, and SMTP (Exchange ActiveSync is not blocked by the policy);
- MFA is required for admins – the policy mandates the usage of MFA for certain administrative tasks.
- End-user protection — the policy allows users to employ multi-factor authentication (MFA) (the user must register for MFA using the Microsoft Authenticator app within 14 days of the first login);
- Require MFA for Service Management — MFA is required for users to login in to Azure Resource Manager API-based services (Azure Portal, Azure CLI, PowerShell).
With a qualifying Azure subscription, you can create your own Conditional Access Policies.
In the Assignments section, you need to specify the conditions for applying the policy.
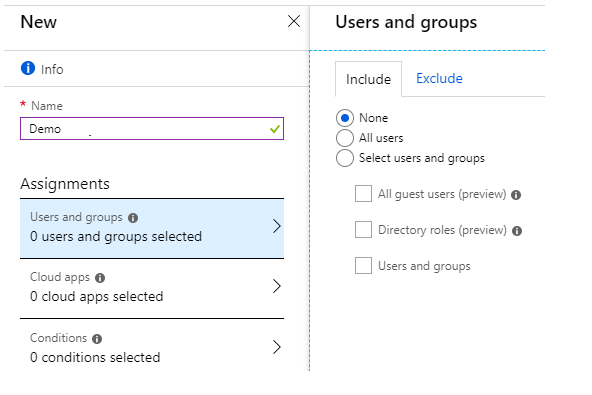
Users and groups — the policy’s coverage of which users. This might be all Azure AD users or specific groups and individuals. Exceptions can be stated in their own section.
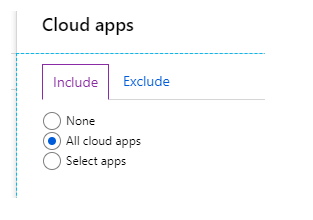
Apps in the cloud – choose from a list of apps that have been registered with Azure AD (you can select more than Office 365 apps)
The Conditions section contains additional conditions.
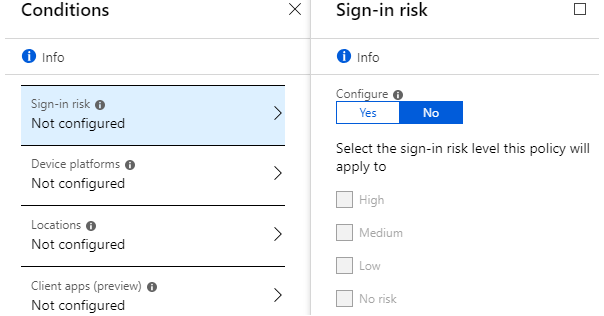
A way for determining the authorisation risk is the sign-in risk (from where, at what time, using which client, how common is this behavior, etc). It’s necessary to have an Azure AD Premium 2 licence.
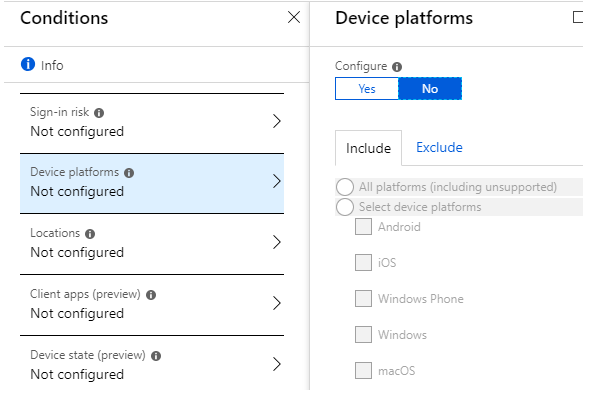
Device platforms — it is possible to specify which platform the policy will apply to (for example, only mobile clients, or only Windows computers
Locations enables you to use trusted IP address lists.
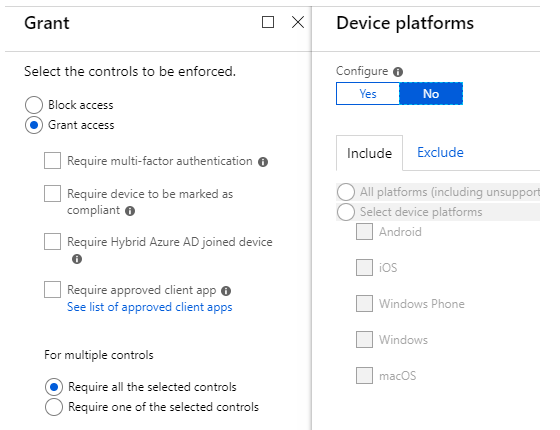
The next step is to define what the policy will accomplish or require.
You can grant or deny access, as well as request and receive additional security measures.
Conditional Access policies may be set up quickly and easily in the Azure Portal. PowerShell can be used in automation deployment scripts or to configure sophisticated CA policies with Microsoft Graph.