When eliminating a domain controller from Active Directory, the DCPromo (demote) operation is recommended because it allows you to erase all records about the old domain controller from the Active Directory database correctly (the computer object, NTDS Settings, site settings, cross-site links and replication metadata).
You can force the removal of a failing domain controller if it fails for some reason and it is not expected to be returned. Metadata cleanup is the term for this operation. You will erase all data about the failing DC from Active Directory Domain Services when you perform metadata cleanup (AD DS). This cleans replication metadata appropriately, including objects in the File Replication Service (FRS) and Distributed File System (DFS) (DFS).
Hint: Make sure there are no FSMO roles on the broken DC, and if required, take these roles and move them to another DC.
You can clear server metadata using the standard Active Directory Users and Computers (dsa.msc) graphical console in a domain with a functional level of Windows Server 2008 R2 or newer.
Simply locate the failed DC in the ADUC console and remove it as if it were an ordinary computer object. Select Delete from the context menu and confirm the deletion.
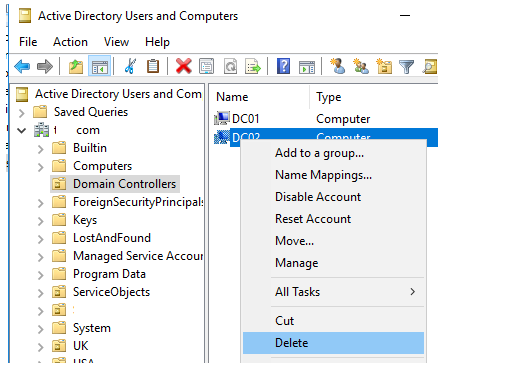
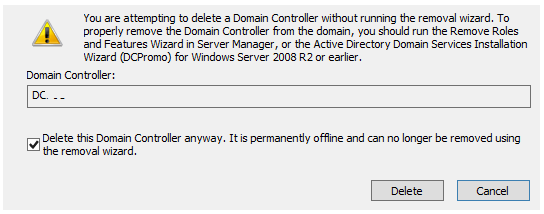
Check the option “This Domain Controller is permanently offline and cannot be downgraded using the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard (DCPROMO)” in the next dialogue box, then click the Delete button.
When attempting to delete a DC, you may receive the following error. “You do not have adequate privileges to delete DC02, or this object is secured against accidental deletion,” double-check:
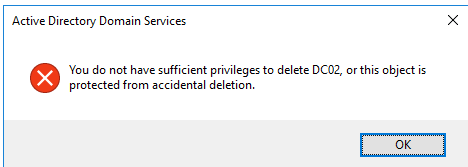
- Your account is a member of the Domain admins group;
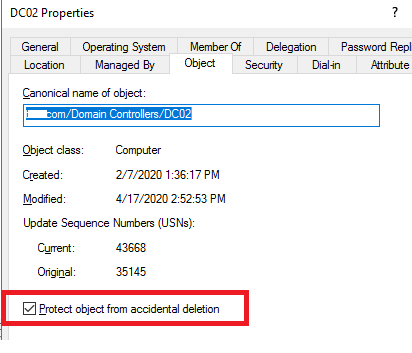
- The option “Protect object from accidental deletion” must be disabled in the object properties (ADUC snap-in > DC > Object tab).
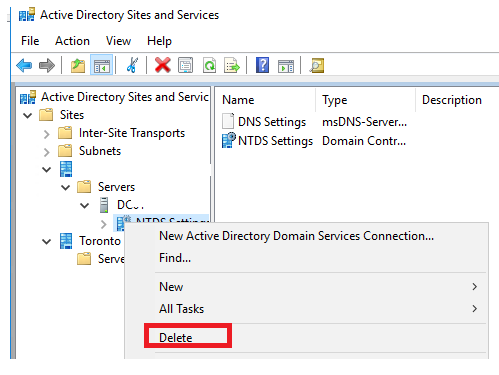
Then open the Active Directory Sites and Services snap-in (dssite.msc) and delete the associated NTDS Settings object (expand the forcefully removed domain controller site, expand Servers > expand the DC name, right click on the NTDS Settings object > Delete). Confirm the object’s deletion.
After that, ADDS will clean up the metadata on its own.
The command-line utility ntdsutil can also be used to clean out server metadata (this is the only correct way to force remove failed DC in domains with a functional level of Windows Server 2008 and lower).
On any of the remaining domain controllers, run command prompt as an administrator.
On the command line, type ntdsutil and click Enter.
One by one, type the following commands:
metadata cleanup
remove selected server <failedDCName># specify the name of the DC to be removed from the AD database
To correctly remove the DC object and information, select Yes.
If you want to quit, type quit.
Check to see if the domain controller has been removed successfully:
- Activate the ADUC console. Verify that the domain controller you deleted is no longer visible in the Domain Controllers container.
- Check if your DC object contains an NTDS Settings object using the Sites and Services snap-in. If this is the case, you can remove the server object from the console.