In a domain network, Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) is a very convenient and valuable cerise. Within your domain, AD CS allows you to issue and manage SSL and other certificates. For Exchange servers, IIS, RDSH farms, and other purposes, you can utilise your own free certificates. We’ll walk you through a simplified scenario for implementing a certification authority in a test environment in this article (it is not recommended to use this manual for a production environment due to a low security). We’ll go through how to install and setup the AD CS role, as well as how to establish a Group Policy for root certificate deployment in a domain.
We do not advocate installing AD CS on an Active Directory domain controller in a production environment. You must deploy the following in a production environment:
- Separate root certification server (Enterprise Root CA): this server issues a certificate to the subordinate CA for signing. It is suggested that this server be turned off (and put in a safe:)) after generating a trusted root certificate and CRL.
- Subordinate CA—this is the organization’s main server for issuing certificates. It can also be used to check revoked certificates by storing a certificate revocation list.
One of the standard Windows Server 2016 roles is Certificate Services. On a domain controller in our test environment, we’ll deploy the AD CS role. The following components of the role must be deployed:
- Certification Authority—certification authority itself;
- Certification Authority Web Enrollment—CSR(certificate hash) certificate issuing web service.
- Launch Server Manager and select Add roles and features;
- Select the current server, in the list of roles check Active Directory Certification Authority and click Next;
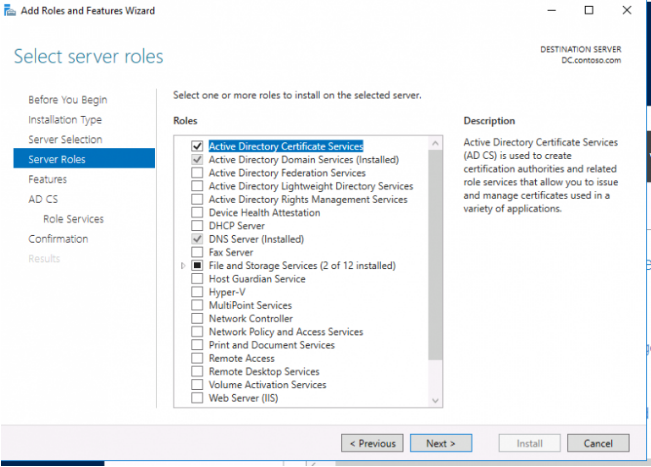
3. In the list of AD CS role components, select:
Certification Authority;
Certification Authority Web Enrollment;
Certification Authority Web Service.
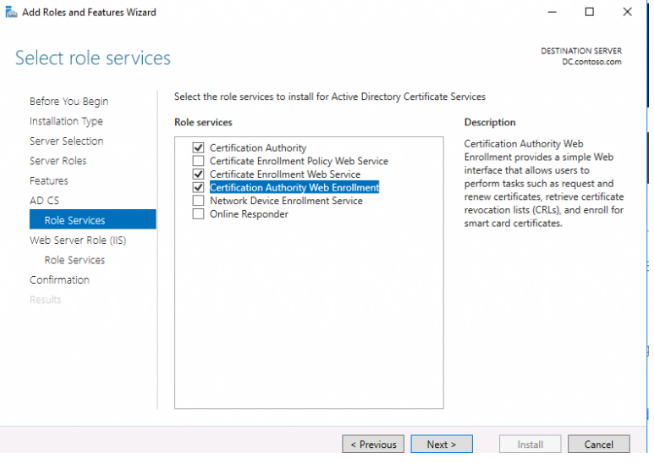
4. Agree to add and install the IIS components that are required;
5. Press the Install button and wait for the necessary components to finish installing.
6. After you’ve finished installing the roles, you’ll need to configure the ADCS role for the first time. To do so, go to Server Manager and select the yellow flag, then Configure Active Directory Certificate Services on the destination server.
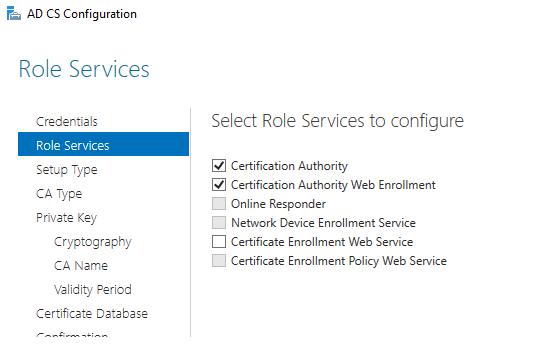
7. Select the services to configure;
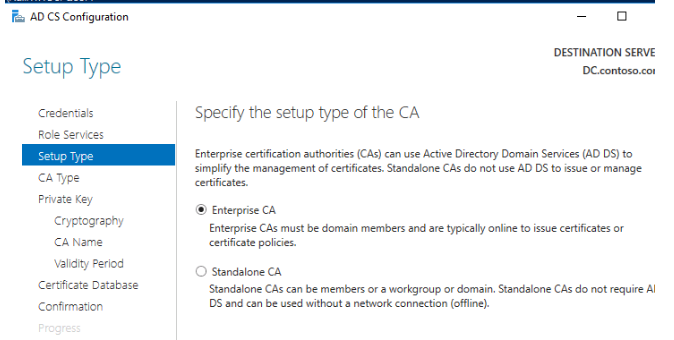
8. Select CA type—Enterprise CA > Root CA;
9. Select Make a fresh private key;
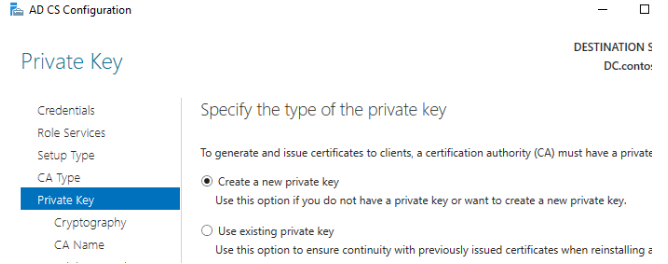
For the private key, leave the default settings:
- RSA provider;
- Key length 2048;
- Hash algorithm: SHA256.
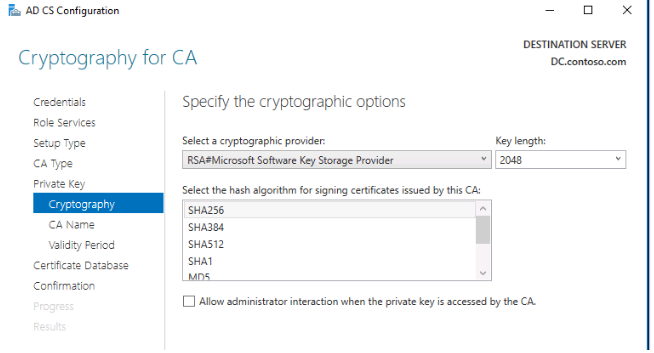
10. The CN name can be left unmodified.
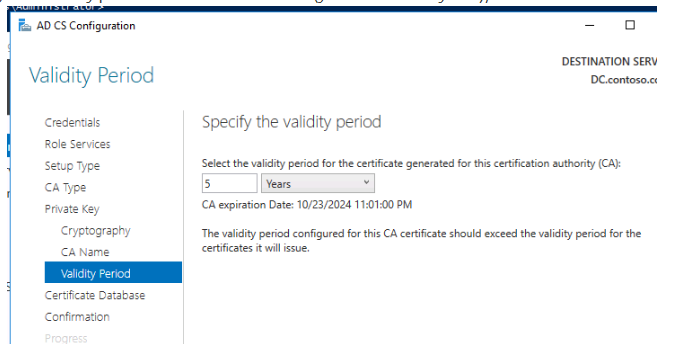
11. Set the CA certificate’s validity time (you can leave it at 5 years);
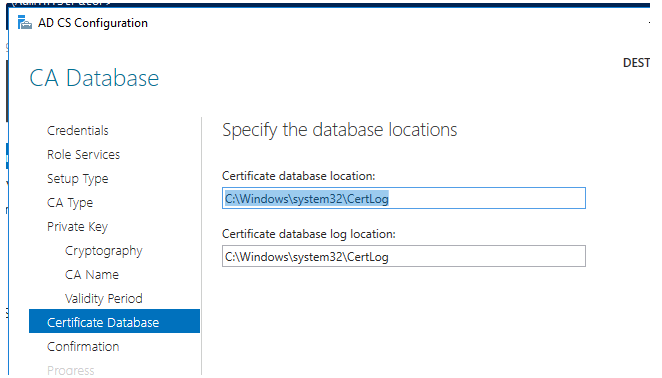
12. Default CA database and log routes should be used: c:windowssystem32certlog
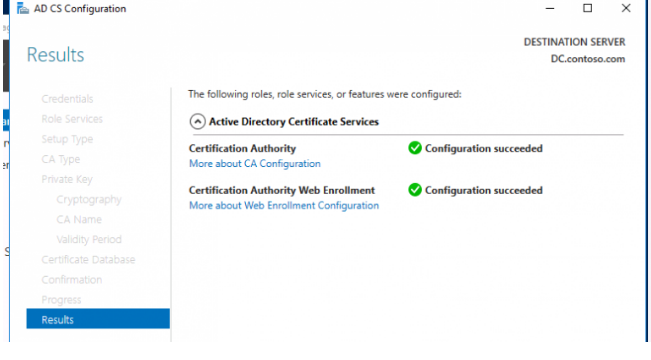
13. If everything is configured correctly, the caption appears: Configuration succeeded.
You can also use PowerShell to install ADCS services. Run the following command to install the AD CS role:
Add-WindowsFeature Adcs-Cert-Authority -IncludeManagementToolsAfter AD CS is installed, run the following command:
Install-AdcsCertificationAuthority -CAType EnterpriseRootCAA unique Certification Authority snap-in is utilised to administer ADCS (you can find it in Administrative Tools). As you can see, the position is currently in progress:
To automatically issue certificates to domain customers, you must now configure autoenrollment domain Group Policy.
- Open the Group Policy Management console, right-click the domain root, and choose “Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…”
- Go to edit mode and give the policy a name.
- To access the section GPO – Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Public Key Policies, go to the section GPO – Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Public Key Policies.
- Choose the “Certificate Services Client – Auto-Enrollment” template.
- Activate the policy and set it up as follows:
- Mode of configuration: Enabled
- Expired certificates should be renewed, pending certificates should be updated, and revoked certificates should be removed.
- After you’ve created this policy, use the gpupdate command to update the policies on the machine domain, and double-check that your root certificate is listed in Trusted Root Certificates.