Domain Naming Master is another forest-wide FSMO position (together with Schema Master), which means that only one domain controller with the Domain Naming Master operation master role can exist in the entire Active Directory forest.
The owner of this job is in charge of Active Directory domain name activities, such as adding, renaming, and removing domains from the forest.
Domain Naming Master
However, there are some duties that are only performed by domain controllers with this role. According to TechNet’s official information, the full list of responsibilities is as follows:
- Domains can be added or removed from the forest — Domains The Naming Master ensures that each domain NETBIOS-name in the forest is unique and prevents domains with the same name from being added. All domain name change activities should be double-checked by the DC owner of this role. You can’t add or remove a domain from the forest if the Naming Master is unavailable.
- Add or remove application directory partitions – starting with the Windows 2003 edition of Active Directory, it was able to construct independent sections called Application Directory Partitions, which are used to store arbitrary data in AD. The data in these parts is likewise replicated to all domain controllers, ensuring greater security and availability. Storage data for DNS servers (Active Directory-Integrated DNS) in the ForestDnsZones and DomainDnsZones sections, for example. When Domain Naming Master isn’t available, you can’t manage application partitions.
ntdsutil
partition management
connect
connect to server lon-dc01
quit
list
3. Cross references (crossRef) are used to search the directory when the server to which the client is connected does not have the requisite copy of the directory, and you can refer to domains outside the forest (of course if they are available). Only the Domain Naming Master has authorization to edit the contents of the Partitions container in the Configuration area, where CrossRefs are stored. Internal and external cross-references are the two forms of cross-references. The system generates internal crossRefs on its own. External cross-references are manually created by the Administrator, who must explicitly define the position of items in the AD forest if necessary. You can’t make a new cross reference or delete an existing one if Domain Naming Master isn’t available.
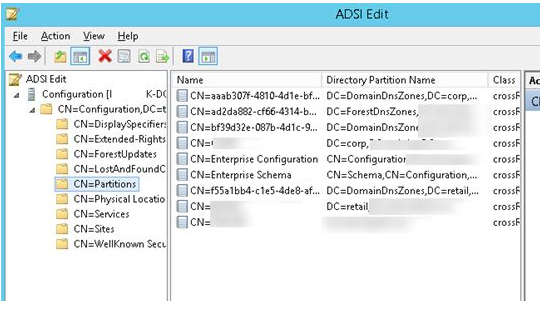
4. Approval of the domain renaming — the software rendom.exe is used to rename a domain. The tool creates an XML script with instructions that must be followed during the renaming procedure. This script is placed in the Configuration section’s container Partitions. Only the domain naming master has access to this container. The new names of each changed domain are then written to the msDS-DnsRootAlias attribute of cross-references of objects associated with these domains.
Using the netdom software, you may find out who currently has the Domain Naming Master role:
netdom query fsmo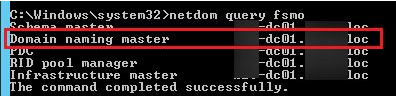
To transfer DNM role from one domain controller to another you can use the Active Directory Domains and Trusts MMC snap-in.
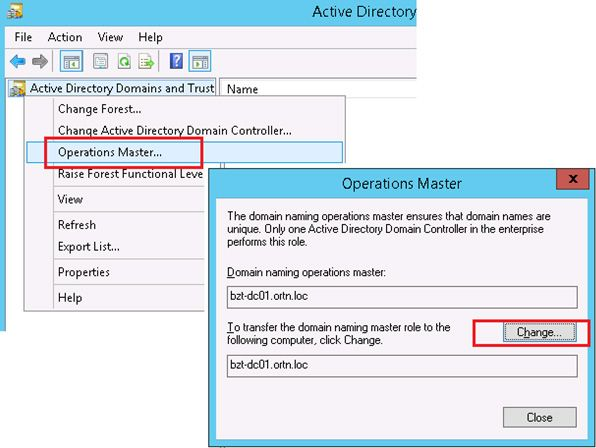
Microsoft recommended that the Domain Naming and Schema Master roles be installed on the same domain controller. If you lose a DC with the FSMO role Domain Naming Master, you can reassign it to another DC, but keep in mind that the original role master should no longer be visible on the network.