In Active Directory, user accounts contain a variety of attributes, including two that are particularly interesting: samAccountName and UserPrincipalName (often referred to as UPN), the differences between which many Windows administrators are unaware of. We’ll look at the differences between the samAccountName and UserPrincipalName AD characteristics in this article.
To log a user into computers in the AD domain, utilize the userPrincipalName and sAMAccountName properties.
In the pre-Windows 2000 environment, the samAccountName attribute was used to specify the user name to authorize on domain servers and workstations. In Windows 2000, however, a new attribute called UserPrincipalName was added, which can be used to log in to AD workstations as well. So you may now use both samAccountName and UserPrincipalName to authorize a PC in the AD domain.
The samAccountName Attribute
The samAccountName attribute has the following format <YOUR_NETBIOS_DOMAIN_NAME><USER_name>. For example, my solutionviews.com domain uses the NetBIOS domain name SOLUTIONVIEWS. Thus, the b.jackson username in the samAccountName format should look like this: SOLUTIONVIEWSb.jackson.
Particulars of the samAccountName attribute:
- Due to backward compatibility, the samAccountName value for a user should not exceed 20 characters (for a computer object, the maximum size of samAccountName is 16 characters). The user login name in the samAccountName element will be trimmed if the account name is more than 20 characters.
- For all domain objects, the value of samAccountName must be unique.
- Even though you signed on to the computer using the UPN, the environment variable percent USERNAME percent on a Windows PC contains the samAccountName attribute value, not UserPrincipalName. The USERNAME environment variable can be used to get the value of SamAccountName on the user’s PC. The set command in cmd or gci env: in PowerShell can be used to display it.
The UserPrincipalName Attribute
The UserPrincipalName attribute has a different format than samAccountName. For instance, in our AD system described above, the value of the user b.jackson’s domain attribute would be b.jackson@solutionviews.com.
- The UserPrincipalName attribute has the following properties:
- The UserPrincipalName parameter can be changed to the user’s e-mail address (which is very useful during migrations, profile settings, and so on);
- The samAccountName attribute’s value must be unique across the whole domain forest.
- The format of the identifier follows the RFC 822 standard;
- The maximum length of a UPN value is not restricted to 20 characters (it can be up to 256 characters);
- Unlike samAccountName, the UserPrincipalName parameter is optional, however it is advised that it be filled up.
When creating a new user in AD, you specify the value of the UserPrincipalName attribute in the “User logon name” and the value samAccountName in the “User logon name (pre-Windows 2000)” field.
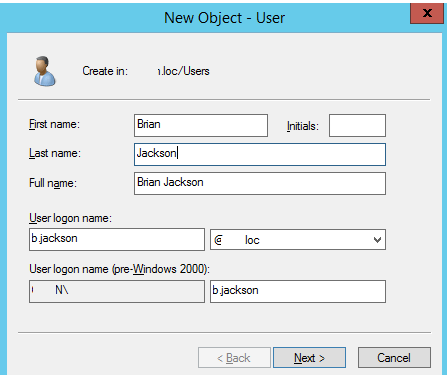
The values of this field can be changed in the future using the ADUC console in the Account tab’s user properties.